XML Save/Load bug fix...
VARNA: Visualization Applet for RNA
A Java lightweight component and applet for drawing the RNA secondary structure
Basic usage
Some of VARNA's main features are demonstrated here, along with the code required to produce them. Have fun!
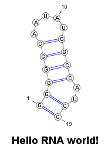
Hello RNA World!
This first examples illustrates the most basic usage of the Applet, which is to display a structure/sequence, along with a title... [More]
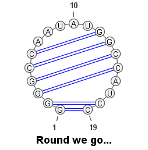
Round we go...
Using a circular layout, specified by assigning a circular value to the algorithm parameter... [More]
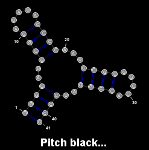
This third example illustrates how one may fully customize the rendering for a given RNA layout... [More]
Funky !
Features a very creative usage of color redefinitions. Additionally, a rotation parameter is defined to orient the drawing correctly... [More]
background
baseOutline
baseInner
baseName
bp
sequenceDBN
structureDBN
rotation
titleColor
title
This code assigns different colors to each panel, while assigning a common sequence/secondary structure and title to every panel. Notice the usage of titleSize to adapt the title width to that of the panel... [More]
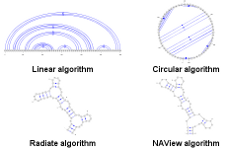
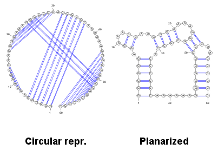
This examples demonstrates the usage of our four different types of representations (layout algorithms) on a single RNA... [More]
Base-pairs styles
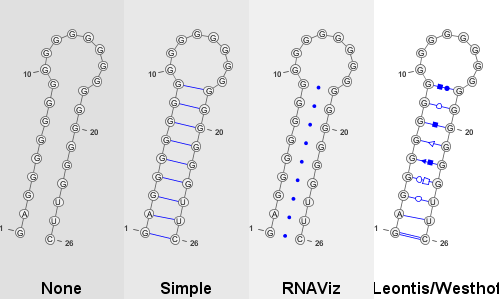
Various base-pairs representations, available through the bpStyle parameter. Non-canonical base-pairs, which cannot be specified by parenthesis expresions, are added through the auxBPs parameter, using the Leontis-Westhof nomenclature... [More]
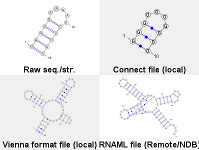
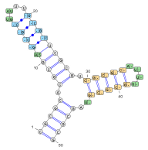
The applet can be configured to fetch the drawn RNA from the internet, by mean of the url parameter. This feature is illustrated in the above example, where four structures are respectively loaded from applet parameters (NW), from the local HTTP server (NE and SW) and from the NDB server (SE)... [More]
Upon loading a pseudoknotted secondary structure, a maximal non-crossing subset of base pairs is extracted and drawn using current algorithm. Remaining base-pairs are drawn in a second-pass, but do not change the coordinates inferred during the initial layout... [More]
Base Styles
Custom styles can be specified for individual base by defining a set of basic styles (basesStyle parameter), later to be applied (applyBasesStyle parameter) on subsets of bases. Alternatively, individual base styles can be set using the customBases parameter... [More]
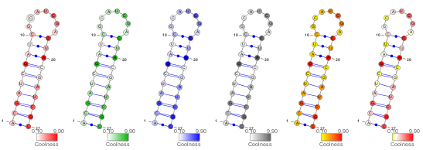
When the colors have a semantic that is related to a numeric value (Conservation, Boltzmann probability...), VARNA offers the possibility to specify these numeric values and automatically maps these values to colors according to a color map... [More]
Adding LabelsIllustrating the different types of textual annotations can be added to a VARNA drawing: Loop, helix, base or static annotations... [More]
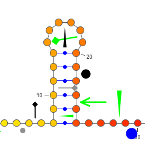
Higlighting RegionsHighlighting regions, ie sequences of contiguous bases, can be useful to draw the reader's attention toward some local remarkable feature... [More]
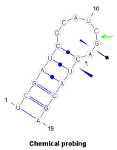
Glyphs
Chemical probing results can be displayed with the chemProb parameter using three types of glyphs: An arrow (type=arrow), a thin triangle (type=triangle) or a pin ending with a diamond (type=pin). Additionally, a custom color (color=#XXYYZZ) and an intensity, denoting the strength of the cleavage (e.g. intensity=1.5) can be specified... [More]
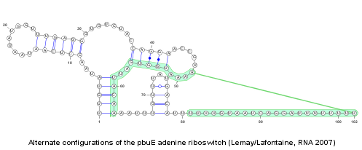
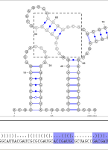
Compatible secondary structures may be jointly represented on a single diagram by annotating their consensus structure... [More]
JS Interactions IVARNA can be used in slave mode, i.e. be controlled by a browser using a set of functions implemented in the dedicated VARNA.js JavaScript library... [More]
Although a VARNA applet cannot easily push information into the browser, a passive looping technique may still be used to let the browser monitor changes occurring within VARNA... [More]
Previous page: Full Features List
Next page: Hello RNA World!